A Deep Reinforcement Learning Environment for Particle Robot Navigation and Object Manipulation
ICRA’22 Outstanding Coordination Paper finalist
Jeremy Shen, Erdong Xiao, Yuchen Liu, Chen Feng
| Abstract | Code | Paper | Results | Acknowledgment |
Abstract
Particle robots are novel biologically-inspired robotic systems where locomotion can be achieved collectively and robustly, but not independently. While its control is currently limited to a hand-crafted policy for basic locomotion tasks, such a multi-robot system could be potentially controlled via Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) for different tasks more efficiently. However, the particle robot system presents a new set of challenges for DRL differing from existing swarm robotics systems: the low degrees of freedom of each robot and the increased necessity of coordination between robots. We present a 2D particle robot simulator using the OpenAI Gym interface and Pymunk as the physics engine, and introduce new tasks and challenges to research the underexplored applications of DRL in the particle robot system. Moreover, we use Stable-baselines3 to provide a set of benchmarks for the tasks. Current baseline DRL algorithms show signs of achieving the tasks but are yet unable to reach the performance of the hand-crafted policy. Further development of DRL algorithms is necessary in order to accomplish the proposed tasks.
Code (GitHub)
The code is copyrighted by the authors. Permission to copy and use
this software for noncommercial use is hereby granted provided: (a)
this notice is retained in all copies, (2) the publication describing
the method (indicated below) is clearly cited, and (3) the
distribution from which the code was obtained is clearly cited. For
all other uses, please contact the authors.
The software code is provided "as is" with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY
expressed or implied. Use at your own risk.
This code provides an implementation of the method described in the
following publication:
Jeremy Shen, Erdong Xiao, Yuchen Liu, and Chen Feng,
"A Deep Reinforcement Learning Environment for Particle Robot Navigation
and Object Manipulation (arXiv)".
How to use
Our environment is developed with OpenAi Gym. Here is a sample simple navigation episode controlled by the handcrafted wave policy.
import math
import gym
from gym_dpr.envs.viz import Visualizer
from gym_dpr.envs.DPR_ParticleRobot import CircularBot
from gym_dpr.envs.DPR_SuperAgent import SuperCircularBot
from gym_dpr.envs.DPR_World import World
env = gym.make('dpr_single-v0',
numBots=9, worldClass=World, botClass=CircularBot, superBotClass=SuperCircularBot,
discreteActionSpace=False, continuousAction=False,
goalFrame=True,
rewardFunc="piecewise",
randomSeed=0,
fixedStart=False, fixedGoal=True,
fixedStartCoords=None, fixedGoalCoords=(0, 0),
polarStartCoords=False, polarGoalCoords=False,
transformRectStart=(0, 0), transformRectGoal=(0, 0),
xLower=-1000, xUpper=1000, yLower=-1000, yUpper=1000,
radiusLower=450, radiusUpper=550, angleLower=0, angleUpper=2 * math.pi,
numDead=0, deadIxs=None,
gate=False, gateSize=150,
manipulationTask=False, objectType="Ball", objectPos=None, initializeObjectTangent=True, objectDims=[100, 30],
visualizer=Visualizer(), recordInfo=True)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
totalSteps, actions = env.wavePolicy() # hand crafted wave policy
for i in range(totalSteps):
for _ in range(10):
action = actions[i]
env.render()
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
if done:
break
env.close()
Paper (arXiv)
To cite our paper:
@misc{https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2203.06464,
doi = {10.48550/ARXIV.2203.06464},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.06464},
author = {Shen, Jeremy and Xiao, Erdong and Liu, Yuchen and Feng, Chen},
keywords = {Robotics (cs.RO), FOS: Computer and information sciences, FOS: Computer and information sciences},
title = {A Deep Reinforcement Learning Environment for Particle Robot Navigation and Object Manipulation},
publisher = {arXiv},
year = {2022},
copyright = {Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International}
}
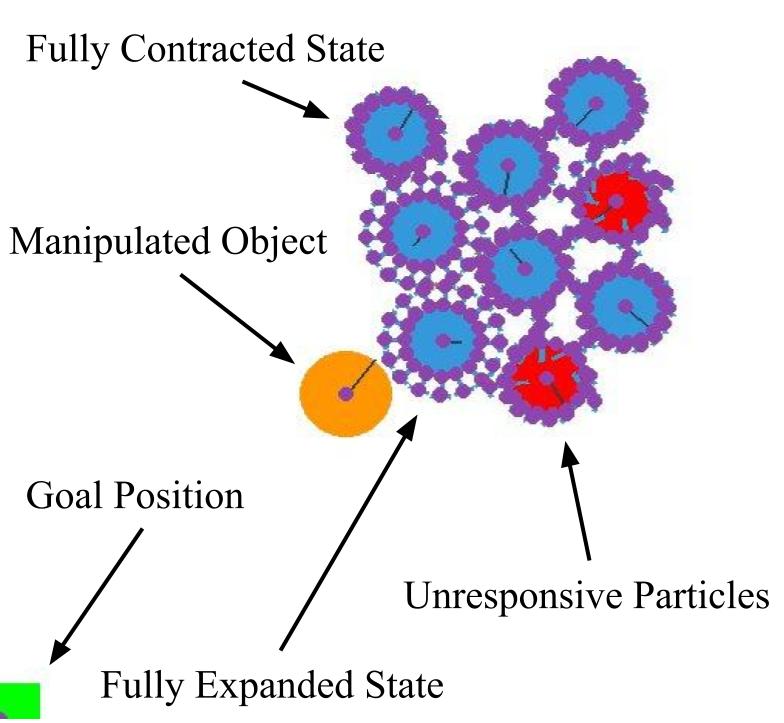
Task environment setups
| Simple Navigation | Obstacle Navigation | Unresponsive Particles | Object Manipulation |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Comparison
There are many reinforcement learning environments out there, but only ours is directly suitable for simulating particle robots.
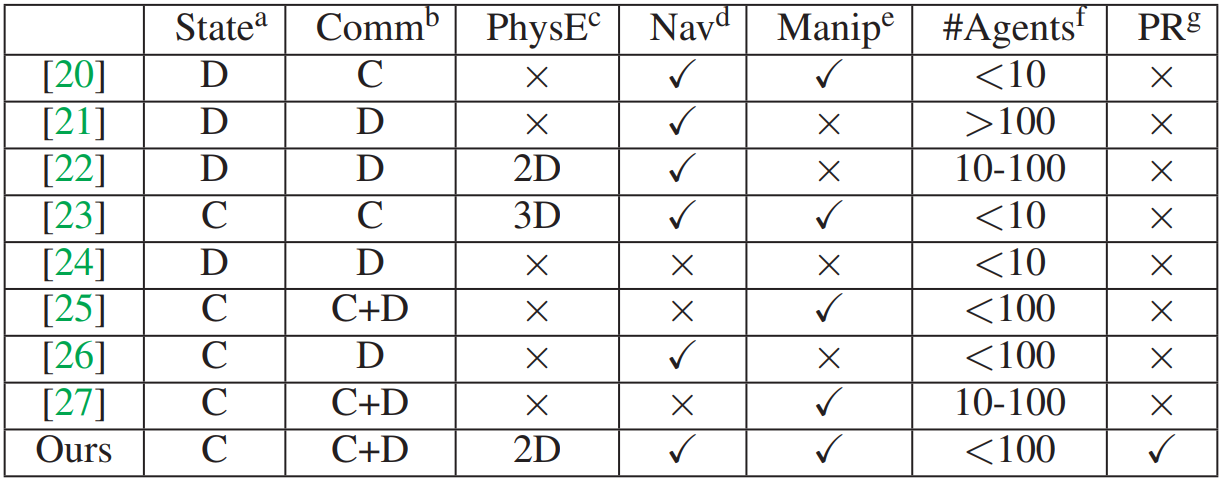
[20] Jiang, S. 2018; [21] Zheng, L. et al. 2017; [22] Lowe, R. et al. 2020; [23] Baker, B. et al. 2020; [24] Playground 2019; [25] Suarez J. 2019; [26] Samvelyan M. 2019; [27] Google Research Football 2019
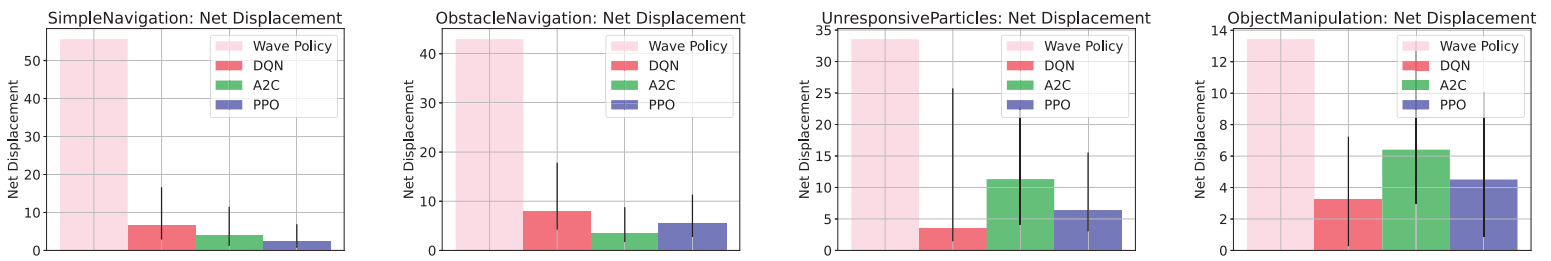
Results
Benchmark results for all four tasks (simple navigation, obstacle navigation, navigation with unresponsive particle robots, and object manipulation). The average, minimum, and maximum displacement is plotted for handcrafted, DQN, A2C, and PPO control.
Sample visualized trials of baselines on simple navigation task.
| Handcrafted | PPO | A2C | DQN |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Acknowledgment
This research is supported by the NSF CPS program under CMMI-1932187.